Last year we presented How to Spoof PDF Signatures. We showed three different attack classes. In cooperation with the CERT-Bund (BSI), we contacted the vendors of affected PDF applications to inform them about the vulnerabilities and to support them in developing countermeasures. Most vendors reacted promptly and closed the reported vulnerabilities promptly.
One of those three attack classes was Incremental Saving Attacks (ISA). The proposed countermeasures aimed to distinguish PDF objects appended to the file via updates into dangerous and non-dangerous. In other words, black and whitelisting approaches were used. Naturally, this countermeasure succeeds as long as the PDF update contains evil objects. So we came up with the idea to attack PDFs with only non-dangerous updates. We achieve this by adding invisible, malicious content when creating the PDF document (before it is signed) and to reveal them after signing.
Today, we present Shadow Attacks! Our evaluation of 28 PDF applications reveals that 15 of them, including Adobe Acrobat and Foxit Reader, are vulnerable.
We responsibly disclosed all affected vendors. Together with the CERT-Bund (BSI), we supported the vendors in developing suitable countermeasures. The attacks are documented in CVE-2020-9592 and CVE-2020-9596.
What are PDF signatures used for and what is the legal status?
PDFs can be secured against manipulations by using digital signatures. This feature enables use-cases such as signing contracts, agreements, payments, and invoices. Regulations like the eSign Act in the USA or the eIDAS regulation in Europe facilitate the acceptance of digitally signed documents by companies and governments. Asian and South American countries also accept digitally signed documents as an equivalent to manually signed paper documents. Adobe Cloud, a leading online service for signing PDF documents, provided 8 billion electronic and digital signature transactions in 2019. The same year, DocuSign processed 15 million documents each day.
What could a Simple Signing Process look like?
The process of digitally signing a contract involves multiple entities and can look as follows: The PDF contract is prepared by the collaborators. The collaborators can be lawyers, designers, typewriters, or members of different companies. Finally, the contract is digitally signed.
PDF Structure and Signature Basics
 |
| A PDF consists of three parts: Body, Xref table, and Trailer |
The PDF is a platform-independent document format. It starts with a Header, to set the version, and is followed by three main parts, as depicted in the figure. The first part defines the PDF Body. It contains different objects, which are identified by its object number. The most important object is the root object, which is called the Catalog. In the figure, the Catalog has the object identifier 1 0. The Catalog defines the whole PDF structure by linking to other objects in the Body. In the example given, the Catalog links to form object AcroForm, to some PDF MetaData, and to actual PDF Pages. The latter can reference multiple Page objects, which in turn reference, for example, the actual Content, Font, and Images. The second part of the PDF is the Xref table. It contains references to the byte positions of all objects used in the PDF Body. The third part is the Trailer. It consists of two further references: one to the byte position at which the Xref table starts, and another link to the identifier of the root object (1 0).
Incremental Updates and Digitally Signing a PDF
The content of a PDF may be updated for different reasons, for example, by adding review comments or by filling out PDF forms. From a technical perspective, it is possible to add this new content directly into the existing PDF Body and add new references in the Xref table. However, this is not the case according to the PDF specification. Changes to a PDF are implemented using Incremental Updates. An Incremental Update adds new objects into a new PDF Body, which is directly appended after the previous Trailer as shown in the figure to the right. To adequately address the new objects, a new Xref table and Trailer are also appended as well for each Incremental Update. Summarized, a PDF can have multiple Bodies, Xref tables, and Trailers, if Incremental Update is applied.
For protecting the integrity and the authenticity of a PDF, digital signatures can be applied. For this purpose, a Signature object is created and appended to the PDF by using Incremental Update. It is also possible to sign a PDF multiple times (e.g., a contract), resulting in multiple Incremental Updates. The Signature object contains all relevant information for validating the signature, such as the algorithms used and the signing certificate. Once a PDF containing a PDF Signature is opened, the viewer application automatically validates the signature and provides a warning if the content has been modified.
Shadow Attacks
The main idea of the attacks is that the attackers prepare a PDF document containing invisible content. Afterward, the document is sent to a signing entity like a person or a service which reviews the document, signs it and sends it back to the attackers. Despite the integrity protection provided by the digital signature, the attackers can make modifications to the document and change the visibility of the hidden content. Nevertheless, the manipulation is not detected. The digital signature remains valid. Finally, the attackers send the modified signed document to the victim. Although the document is altered, the signature validation is successful, but the victims see different content than the signing entity.
Do the Attacks match a Real-World Scenario?
Of course! In companies and authorities, relevant documents like contracts or agreements are often prepared by the employees who take care of most of the details and technicalities. The document is then signed by an authorized person after a careful review. Another scenario is the signing process of a document within a consortium. Usually, one participant creates the final version of the document, which is then signed by all consortium members. Considering the given examples, an employee or consortium member acting maliciously can hide invisible shadow content during the editing. Consequentially, this content will be signed later.
Additionally, multiple cloud signing services like Adobe Cloud, DocuSign, or Digital Signature Service exist. Among other functionalities, such services receive a document and sign it. This process can also be used also to sign shadow documents.
Different Attack Classes of Shadow Attacks
Shadow Attacks can be divided into the three attack classes Hide, Replace, and Hide-and-Replace, as shown in the figure below. Each class offers the possibility of taking a significant influence on the content of a signed PDF document. In the following, we describe the functionality of the individual classes in more detail.
Shadow Attack: Hide
The concept of this class of shadow attacks is to hide the content relevant for the victims behind a visible layer. For example, the attackers can hide the text "You are fired!" behind a full-page picture showing "Sign me to get the reward!". Once the attackers receive the signed document, they manipulate the document in such a way that the picture is no longer rendered by the viewer application. Hide attacks have two advantages from the attackers' perspective: - Many viewers show warnings if new visible content is added using an Incremental Update. However, they do not warn in most cases if content is removed.
- The objects are still accessible within the PDF. In the example above, the text "You are fired!" can still be detected by a search function. This might be important if an online signing service is used and it reviews the document by searching for specific keywords. We identified two variants of this attack class.
Hiding Content via Page.
This attack variant uses an Incremental Update to create a new Page object. It contains all previously used objects except for the overlay, for example, the image. This attack variant is depicted on the left side of figure above. Hiding Content via Xref.
If the viewer application does not accept changes to PDF structuring objects, such as Page, Pages, or Contents, the second attack variant can be applied. This variant directly affects the overlay object. The simplest method for this is to create an Incremental Update, which only updates the Xref table by setting the overlay object to free. However, making this change is interpreted as a dangerous in many viewers (e.g., Adobe) and an error or a warning is thrown. For this reason, we use another approach: we use the same object ID within the Incremental Update, but we define it as a different object type. For example, we change the overlay type Image to XML/Metadata.
When opening this manipulated document, the overlay is hidden because Metadata cannot be shown. Since adding Metadata to a signed PDF using Incremental Update is considered harmless, the signature remains valid.
Shadow Attack: Replace
In this attack class, specific content of the PDF document is to be exchanged. The first variant uses the visual properties of text fields for this purpose. The second variant is based on a fatal misconception that fonts cannot be used for manipulation purposes.
Replace via Overlay. This attack targets an interactive feature in PDFs: interactive forms. Forms support different input masks (e.g., text fields, text areas, radio/selection buttons) where users dynamically enter new content and store it in the PDF document. The main idea of the attack is to create a form, which shows one value before (PDF1) and after signing (PDF2), as illustrated on the leftside in the figure below. After the attackers manipulate the PDF and create PDF3, different values are shown in the form (and can be seen on the right side of the figure below). The attack abuses a special property of PDF text fields. A text field can show two different values: the real field value and an overlay value which disappears as soon as the text field is selected. The real value of a form field is contained in an object key named /V. The content of the overlay element is defined within a /BBox object. The /BBox object is comparable to the hint labels known from HTML forms; for example, the hint username to indicate that the username should be entered into a specific login field. In contrast to HTML, in PDF there is no visual difference between the hint and the actual value. 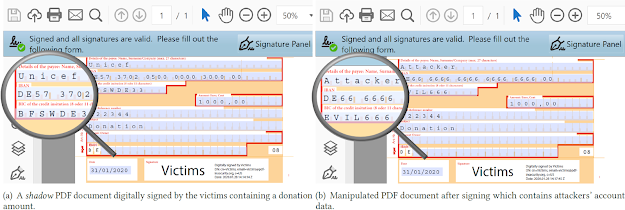
In summary, we can say that this variant allows attackers to manipulate the contents of the text fields for the visible layer arbitrary. As shown in the figure above, this can be used, for example, to maliciously redirect a payment. Replace via Overwrite.
The main idea of this variant is to append new objects to the signed document which are considered harmless but directly influence the presentation of the signed content. As shown in figure of the three attack classes, the attackers prepare a shadow document that defines a font and includes its description into the document. The font is used for the presentation of specific content. After the document is signed, the attackers append a new font description and overwrite the previous description. The definition of new fonts is considered harmless, because of that, the applications verifying the signature do not show any warning regarding the made changes. For instance, the (re)definition of fonts does not change the content directly. However, it influences the view of the displayed content and makes number or character swapping possible.
Shadow Attack: Hide-and-Replace
In this attack class, the attackers create a shadow PDF document that is sent to the signers. The PDF document contains a hidden description of another document with different content. Since the signers cannot detect the hidden (malicious) content, they sign the document. After signing, the attackers receive the document and only append a new Xref table and Trailer. Within the Xref table, only one change takes place: the reference to the document Catalog (or any other hidden object), which now points to the shadow document. In fact, the document contains two independent content paths. One path to show the signer harmless content, and one path with malicious content that replaces the first content after it is signed and activated by the attackers. The figure above visually illustrates the described relationships once again. This attack variant is the most powerful one since the content of the entire document can be exchanged, including text content, forms, fonts, and annotations. The attackers can build a complete shadow document influencing the presentation of each page and each object.
Evaluation
Overall, 15 out of 28 PDF viewing applications were vulnerable to at least one presented attack. Surprisingly, for 11 PDF viewers, all three attack classes were successful. The Table shows that some applications have limited vulnerabilities. These applications respond to any type of Incremental Update with a post-signature modification note, including modifications that are allowed due to the specification. We have evaluated the latest (at the time of evaluation) available versions of the applications on all supported desktop platforms: Windows, macOS, and Linux.  |
| Evaluation results. |
Authors of this Post
Simon Rohlmann
Christian Mainka
Vladislav Mladenov
Jörg Schwenk
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to the CERT-Bund (BSI) team for the great support during the responsible disclosure. We also want to acknowledge the teams of the vendors which reacted to our report and fixed the vulnerable implementations.
Related news- Hacking Tools For Windows
- Hacking Tools For Windows Free Download
- Hacker Tools Mac
- Pentest Tools Review
- Pentest Tools Github
- Hacks And Tools
- Hacking Tools For Pc
- Hacking Tools Kit
- Pentest Tools Online
- How To Hack
- Hacker Tools Online
- New Hacker Tools
- Hacking Tools For Windows 7
- Android Hack Tools Github
- Hacking Tools Software
- Physical Pentest Tools
- Github Hacking Tools
- Pentest Tools Tcp Port Scanner
- Hacking Tools Free Download
- Black Hat Hacker Tools
- Pentest Reporting Tools
- Hackers Toolbox
- Game Hacking
- Best Hacking Tools 2019
- Hacker Tools Free Download
- Hack Tools For Pc
- Hacker Tools 2020
- Pentest Tools Nmap
- Pentest Tools Port Scanner
- Pentest Tools
- Pentest Tools For Windows
- Hacker Security Tools
- Hack Tools For Mac
- Hacker Tools Apk
- Hacker Tools For Windows
- Hack Rom Tools
- World No 1 Hacker Software
- What Are Hacking Tools
- Pentest Box Tools Download
- Hacking Tools Mac
- Hacker Tools For Ios
- New Hacker Tools
- Hacking Tools For Windows Free Download
- Pentest Tools
- Hacking Tools For Games
- Hacker
- Hack Tools Pc
- Nsa Hack Tools
- Hacking Tools Pc
- Hack Tools Pc
- New Hacker Tools
- Pentest Tools Url Fuzzer
- Usb Pentest Tools
- Pentest Tools Online
- Hacker Tools Apk Download
- Hack Tools For Windows
- Hacking Tools Windows 10
- Pentest Tools Subdomain
- World No 1 Hacker Software
- Pentest Tools Alternative
- Pentest Tools
- Hacking Apps
- Pentest Tools Android
- Pentest Tools Android
- Android Hack Tools Github
- Hacking Tools Windows
- Pentest Tools For Windows
- New Hack Tools
- Pentest Tools For Android
- Physical Pentest Tools
- Kik Hack Tools
- Pentest Tools Android
- Termux Hacking Tools 2019
- Hackers Toolbox
- Github Hacking Tools
- Hack Tools Online
- Hack Tools Pc
- Hacker Tools Free
- Nsa Hack Tools
- Game Hacking
- Usb Pentest Tools
- Hack Apps
- Hack Tools Github
- Hacking Tools Hardware
- Hacker Tools For Mac
- Pentest Tools Download
- Pentest Tools Online
- Hak5 Tools
- Pentest Tools For Ubuntu
- Bluetooth Hacking Tools Kali